With a variety on the shelves of the country, they remain out of competition due to efficiency and durability. However, a quality product is not always purchased, because in the store you cannot disassemble the goods for inspection. And in this case, it is not a fact that everyone will determine from what parts it is assembled. burn out, and it becomes expensive to buy new ones. The solution is to repair LED lamps with your own hands. This work is within the power of even a novice home master, and the details are inexpensive. Today we will figure out how to check in which cases the product is being repaired and how to do it.
It is known that LEDs cannot work directly from a 220 V network. To do this, they need additional equipment, which, most often, fails. We'll talk about him today. Consider the scheme, without which the operation of the lighting device is impossible. Along the way, we will conduct an educational program for those who do not understand anything in radio electronics.

driver gauss 12w
The 220V LED lamp driver circuit consists of:
- diode bridge;
- resistance;
- resistors.
The diode bridge serves to rectify the current (turns it from AC to DC). On the graph, this looks like cutting off a half-wave of a sinusoid. Resistances limit the current, and capacitors store energy by increasing the frequency. Consider the principle of operation on the diagram of a 220 V LED lamp.
The principle of operation of the driver in the LED lamp
| Diagram view | Operating procedure |
 | The 220V voltage is applied to the driver and passes through a smoothing capacitor and current limiting resistor. This is necessary in order to secure the diode bridge. |
 | Voltage is applied to a diode bridge, consisting of four multidirectional diodes that cut off the half-wave of the sinusoid. The output current is constant. |
 | Now, by means of a resistance and a capacitor, the current is again limited and the desired frequency is set to it. |
 | Voltage with the necessary parameters is supplied to equidirectional light diodes, which also serve as a current limiter. Those. when one of them burns out, the voltage rises, which leads to the failure of the capacitor if it is not powerful enough. This happens in Chinese products. High-quality devices are protected from this. |
Having understood the principle of operation and the driver circuit, the decision on how to fix a 220V LED lamp will no longer seem difficult. If we talk about quality, then you should not expect trouble from them. They work all the prescribed time and do not fade, although there are “diseases” to which they are also subject. Let's talk about how to deal with them.
Causes of failure of LED lighting devices
To make it easier to understand the reasons, we summarize all the data in one common table.
| Cause of failure | Description | Solution |
| Voltage drops | Such lamps are less prone to breakdowns due to voltage drops, however, sensitive surges can “break through” the diode bridge. As a result, the LED elements burn out. | If the jumps are sensitive, you need to install, which will significantly extend the life of the lighting equipment, but also other household appliances. |
| Wrong lamp selected | Lack of proper ventilation affects the driver. The heat generated by them is not removed. As a result, overheating occurs. | Choose with good ventilation, which will provide the desired heat transfer. |
| Mounting errors | Incorrectly selected lighting system, its connection. Incorrectly calculated cross-section of electrical wiring. | Here, the solution is to unload the lighting line or replace lighting fixtures with devices that consume less power. |
| External factor | Increased humidity, vibration, shock or dust due to incorrect selection of IP. | Proper selection or elimination of negative factors. |
Good to know! Repair of LED lamps cannot be done indefinitely. It is much easier to eliminate negative factors affecting durability and not to buy cheap products. Savings today will cost tomorrow. As economist Adam Smith said, "I'm not rich enough to buy cheap things."

Do-it-yourself repair of a 220 V LED lamp: the nuances of work
Before you repair the LED lamp with your own hands, pay attention to some details that require less labor. Checking the cartridge and the voltage in it is the first thing to do.
Important! Repair of LED lamps requires a multimeter - without it, it will not be possible to ring out the driver elements. You will also need a soldering station.
household multimeters
A soldering station is needed to repair LED chandeliers and fixtures. After all, overheating of their elements leads to failure. The heating temperature during soldering should be no higher than 2600, while the soldering iron heats up more. But there is a way out. We use a piece of copper core with a cross section of 4 mm, which is wound around the soldering iron tip with a dense spiral. The more you lengthen the sting, the lower its temperature. It is convenient if the multimeter has a thermometer function. In this case, it can be adjusted more precisely.

Soldering Station
But before you repair LED spotlights, chandeliers or lamps, you need to determine the cause of the failure.
How to disassemble an LED light bulb
One of the problems that a novice home master faces is how to disassemble an LED light bulb. To do this, you will need an awl, a solvent and a syringe with a needle. The diffuser of the LED lamp is glued to the body with a sealant that needs to be removed. Sweeping gently along the edge of the diffuser with an awl, we inject the solvent with a syringe. After 2÷3 minutes, twisting lightly, the diffuser is removed.

Some lighting fixtures are made without gluing with sealant. In this case, it is enough to turn the diffuser and remove it from the housing.
We identify the cause of the failure of the LED light bulb
After disassembling the lighting fixture, pay attention to the LED elements. Often burned is determined visually: it has tan marks or black dots. Then we change the faulty part and check the performance. We will tell you in detail about the replacement in the step-by-step instructions.
If the LED elements are in order, go to the driver. To check the performance of its parts, you need to unsolder them from the printed circuit board. The value of the resistors (resistances) is indicated on the board, and the parameters of the capacitor are indicated on the case. When dialing with a multimeter in the corresponding modes, there should be no deviations. However, often failed capacitors are determined visually - they swell or burst. The solution is to replace it with a suitable one according to technical parameters.

Replacing capacitors and resistances, unlike LEDs, is often done with a conventional soldering iron. In this case, care should be taken not to overheat the nearest contacts and elements.
Replacing light bulb LEDs: how difficult is it
If you have a soldering station or a hair dryer, this job is easy. It is more difficult to work with a soldering iron, but it is also possible.
Good to know! If there are no working LED elements at hand, you can install a jumper instead of the burnt one. Such a lamp will not work for a long time, but it will be possible to win some time. However, such repairs are made only if the number of elements is more than six. Otherwise, the day is the maximum work of the repair product.
Modern lamps run on SMD LED elements that can be soldered from the LED strip. But it is worth choosing the ones that are suitable for technical characteristics. If there are none, it is better to change everything.

Related article:
For the correct choice of LED devices, you need to know not only the general ones. Useful information about modern models, electrical circuits of working devices. In this article, you will find answers to these and other practical questions.
Repair of the LED lamp driver in the presence of the electrical circuit of the device
If the driver consists of SMD components that are smaller, we will use a soldering iron with a copper wire on the tip. During a visual inspection, a burnt element was revealed - we solder it and select the appropriate one according to the marking. No visible damage - it's more difficult. We'll have to solder all the details and call separately. Having found a burnt one, we change it to a workable one and. It is convenient to use tweezers for this.
Helpful advice! Do not remove all elements from the printed circuit board at the same time. They are similar in appearance, you can later confuse the location. It is better to solder the elements one at a time and, after checking, mount them in place.

How to check and replace the power supply of LED lamps
When installing lighting in rooms with high humidity (or), stabilizing ones are used, which lower the voltage to a safe one (12 or 24 volts). The stabilizer can fail for several reasons. The main ones are excessive load (power consumption of luminaires) or incorrect choice of the block protection degree. Such devices are repaired in specialized services. At home, this is unrealistic without the availability of equipment and knowledge in the field of radio electronics. In this case, the PSU will have to be replaced.

Power supply for LEDs
Very important! All work on replacing the stabilizing LED power supply is carried out with the voltage removed. Do not rely on the switch - it may be incorrectly connected. The voltage is turned off in the switchboard of the apartment. Remember that touching live parts with your hand is life threatening.
It is necessary to pay attention to the technical characteristics of the device - the power must exceed the parameters of the lamps that are powered by it. Having disconnected the failed unit, we connect a new one according to the diagram. It is located in the technical documentation of the device. This does not present any difficulties - all wires are color-coded, and the contacts are lettered.
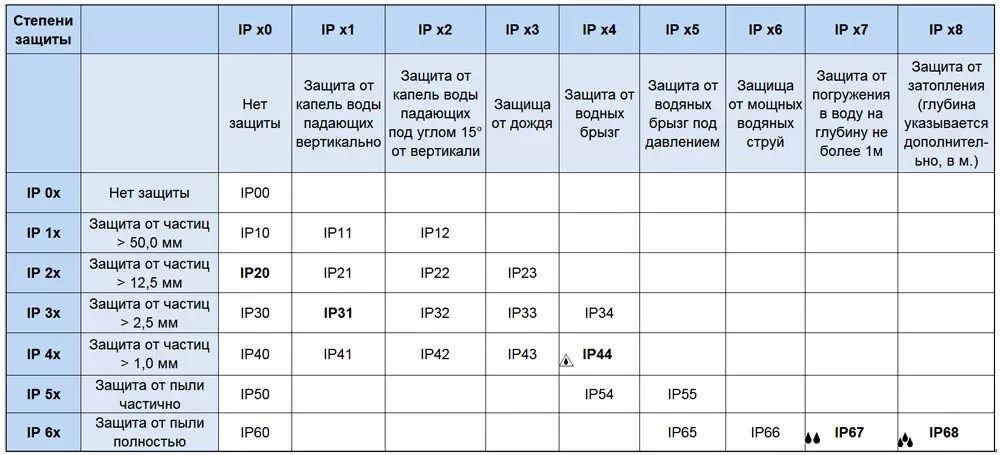
The degree of protection of the device (IP) also plays a role. For the bathroom, the appliance must be marked at least IP45.
Article
Hello! Today I want to tell you about how to correctly connect and properly operate spotlights, chandeliers, sconces, and more.
I will also try to explain in an accessible way why light bulbs burn out quickly. Today, due to a violation during the installation of electrical wiring for lighting, the issue of quickly burning light bulbs is becoming more and more acute.
Let's start with spotlights.
since this is the most popular way of lighting in modern apartments, and spotlights are placed not only on the ceilings to illuminate the apartment itself, but they are also installed in various furniture for lighting - cabinets, sideboards, kitchen sets. The list is endless.
Why do light bulbs burn out so often at points?
And there can be a lot of reasons for this disease, especially if you have halogen bulbs. Such lamps are especially capricious with illiterate installation.


1) First reason this is the wrong connection scheme (connection) of spotlights. When all points are connected to one wire one after another. With this scheme, the load of each subsequent lamp falls on the connection of the previous one. And the total load of all lamps falls on one wire. This is visible on the diagram.

This connection scheme is not correct, and often leads to the rapid burnout of conventional incandescent and halogen bulbs. Nevertheless, this scheme is used everywhere and by everyone, from lighting in cabinets to lighting a room.
What happens with such a connection? And this is what happens: Let's say that on the first light bulb from the side of the junction box, the contacts of the cartridge are oxidized from the strong heating of the halogen (the temperature is high there, and the cartridge is naturally Chinese - overheating cannot be avoided), then a chain reaction begins, the wires coming from the cartridge gradually begin to warm up, then the connection to the common wire is heated. And when the connection is heated, the oxidation of the interconnected wires will not take long. Here, too, the following lamps give a large load on an already heated connection. Accordingly, due to the heating and subsequent oxidation of the connection, the resistance between the connected wires increases, voltage drops occur on this line, which lead to frequent burnout of the light bulbs.
And with the correct connection scheme, a separate wire goes from the junction box to each lamp. In this case, the load is distributed evenly. Seen in the diagram below

But if you have completed the first scheme and there is no way to fix it, then I recommend this procedure to my clients: I remove spotlights from the ceiling (cabinet, headset), cut off the oxidized part of the wire and throw out the old cartridges from all points, install new ones cartridges and connect the chain. But I advise you to refuse halogen bulbs and incandescent lamps, otherwise the problem with burnout with such a connection scheme will again not be long in coming. And I install LED lamps instead of halogens.

They are not afraid of voltage surges, although there will be no surges, since LED lamps are slightly higher than room temperature, even with prolonged use. And they work up to five years. The average price of such a lamp in Ufa is 200 rubles, which will easily pay off for a given period of work. At the same time, you will save on electricity, since the LED consumes significantly less incandescent and halogen lamps (almost does not consume at all). Here you are saved. Everything is easy and simple to treat.
The most important thing is that LEDs come in a variety of shapes, so you can easily match them to your old fittings from spotlights.

This is another savings.
And we turn to the second reason for the frequent burnout of lamps.
2) The second reason, due to the poor type of connection of spotlights to the supply wires. These are the so-called twists (this is usually done always). With a simple twisting of the wires, even the correct connection diagram will not help, the bulbs will still burn out (halogens, incandescent lamps).
And what happens when twisting? now I will try to explain. The first thing that comes to mind is the natural oxidation of twisted wires, even with a very tight twist, the darkening of copper is always visible, the wires literally darken over time. This is visible to the naked eye. And oxidation leads to an increase in the transition resistance at the junctions of the wires. Again, this all leads to a voltage drop and the rapid destruction of the lamp.
But there is another reason not to put the wires on twists, and this reason is called "Eddy currents", arising in our twist, since it is something like "coil - inductance", Roughly speaking. Well, as always, this leads to interference and further - further - further to the consequences that you have already guessed.
Well, it is also not difficult to treat. The lamp is removed from the ceiling, the cartridge is replaced, the twists are cut off, and the wires are connected in a new way, but already tightened through the immortal terminal block.

Well, when you combine these two rules (circuit and correct connection), even halogens will work for you for a long time. Although usually not two rules are combined, but these two errors. Brrrr, even this paradox becomes unpleasant.
And now I’ll move a little away from the topic of burning light bulbs, and I’ll come to the case when the light disappears simultaneously in all lamps. Usually this often happens, but do not rush to buy new light bulbs, because it is most likely not about them.
Usually the reason for the simultaneous shutdown of the fixtures is either a break in the supply cable, or most likely your step-down transformer has failed.

Such a transformer is installed if the fittings and the halogen or LED lamp are designed for a voltage of 12 V. And since transformers are usually selected mainly at the lowest price, they often fail. The owners over and over again after each breakdown have to call the master to replace the step-down transformer. In this case, I suggest that the owners replace the torment with the transformer, by completely removing it, and connecting the fixtures directly. But at the same time, it is necessary to replace 12-volt bulbs with 220-volt ones.
Let's go directly to the chandeliers
Namely, let's start with Chinese budget chandeliers with LED backlighting, halogen bulbs and a seductive remote control.

Such a filling for a low price naturally gives rise to a lot of problems regarding the quality of the product. And in the first place we have burning halogens (light bulbs), this problem is the first symptom of a complete breakdown of the chandelier. The reasons are basically the same - at first, due to strong overheating from the lamps, the contacts of the cartridges lose their elasticity (this is due to the quality of the metal of the contacts), when the elasticity is lost, the contacts weakly compress the pins of our halogens. Which leads to poor contact and further, constant burning of the lamps. You can put up with all this, and light bulbs, in principle, are not so expensive, you can buy it, but we are replacing the harmless combustion of lamps with another, more serious one. In the chandelier, after this stage, its electrical wiring starts to get very hot, and since the wiring in it is very thin, they literally smolder. And when the time comes for the insulation to melt, the entire bundle of wires fuses together, thereby causing a short circuit. In some cases, the chandelier completely stops working, as the step-down transformer fails, in some situations several lamps remain working, or only the backlight works. In this case, it is necessary to change all the wiring of the chandelier, as well as cartridges and a transformer with a control unit. But this process is rather laborious, and most often it is not possible to extract the cartridges.
Here is a typical post from one of the "LED" forums:
- I changed the lamps in the car to LEDs (no driver, stupidly lowering resistances) in the interior ceiling, dimensions and trunk lighting, after 3-4 months the ceiling in the cabin began to flicker (it blinks like a strobe, one line of SMD diodes, then two), then the same turbidity with one dimension occurred .... I changed the lamp in the ceiling for a new one - after 2 months the effect repeated ... The question is - why is this happening? Is it the quality of the components or is there another problem?
Let's try to figure it out! And let's start with theory. The LED is powered by a strictly defined current, which is normalized by the manufacturer. Less is possible, more is not! Therefore, in series with the “garland” of diodes, an element is included that limits or stabilizes the current through them to the value recommended by the diode manufacturer.
Actually, there are no complaints about the durability of diodes in lamps with a built-in current stabilizer (which is often called a “driver”). However, most low-power LED lamps sold today (side lights, interior lighting, dashboard, turn signals, etc.) are lamps made without a “driver”, according to a simplified scheme: not with a current stabilizer, but with a limiter, the role performed by a simple resistor. With it, the circuit of the simplest low-power diode light bulb looks like this:
The most typical malfunctions of such LED lamps:
- Complete burnout - the failure of one diode in the chain. If there is only one circuit in the lamp, then due to the combustion of any of the diodes, the series circuit is broken, and the lamp goes out entirely.
- Partial burnout - failure of one of the chains, if there are several of them in the lamp. Does not cause extinction, but the brightness drops.
- Flicker-“stroboscope” is a kind of defect of a “dying” diode in a chain, when the p-n-structure of the crystal changes due to overheating - an unstable region is formed on the semiconductor, sometimes passing current, sometimes not ...
So why do LED bulbs burn out? What is the problem of their fragility? The fact that manufacturers do not use current stabilizers, but use elementary resistor limiters? Partly yes... but not only!
Even the simplest resistor performs its function well as a “body armor” for LEDs, protecting them from excess current and premature death. But only if:
- The value of this resistor is correctly calculated and provides a safe current through the diodes;
- The supply voltage is stable.
But often there is neither one nor the other ... Chinese unfortunate engineers know that car owners, as a rule, buy LED bulbs according to the principle: “Turn it on for me, I'll see how it shines!”. And the sellers are ready to meet the needs of the buyers - they always have a special stand with a variety of cartridges and a battery at hand, on which they are ready to light any lamp for testing. And since the client “loves with his eyes”, then lamp manufacturers argue as follows - you need to put such a current-limiting resistor so that the lamp lights up with a desperate light and looks attractive even at 10-11 volts of an old battery supplying the stand that has not been charged for a long time!
As a result, the lamp diodes, even at 12 volts, ALREADY work with overload, and after the engine is started, the voltage in the on-board network that feeds the diodes rises from 12 to 14.2 volts - and this, for a minute, is almost 20% difference! The current has grown - already to dangerous values. The current increased - the temperature of the diode crystals increased, which gave an avalanche-like increase in the current - and the diodes switched to wear mode!
Let's move on to practice!
To demonstrate what it looks like, let's move on to experiments - elementary, but visual! Let's just apply a standard voltage of 14.2 volts to a few randomly purchased diode lamps and look at the current consumed by the lamp, heating the lamp and further increasing the current.
Let's test a couple of different models of W5W lamps, a C5W lamp, a C5W lamp-panel, as well as waterproof lamps in a bolt-on housing, designed for mounting in a bumper as a DHL:

To begin with, we take a lamp in the form of an LED module-panel with an external base, like the rod lamps of the C5W and C10W types. It is assumed that this module can be pushed into the ceiling light of the car and connected to the contacts intended for the standard C5W. The module is ready, molded on double-sided tape, designed for easy do-it-yourself installation.

When 14.2 volts is applied to the lamp, it literally hits the eyes with unhealthy light and rapidly heats up in the hands - the current consumed when turned on is 0.58 amperes (more than 8 watts) and continuously grows from the self-heating of the crystals - after a couple of minutes it reaches 0, 71 amps (that's already 10 watts!) and continues to rise. It becomes impossible to hold the lamp in your hand even for a second, which indicates that the temperature has exceeded 70-80 degrees, and this is not the limit ... The fact that the diodes are mounted on an aluminum board, which supposedly serves as a good heat sink, does not help them at all !

Conclusion: in pursuit of brightness, the Chinese powered the diodes in the lamp with an extreme current that exceeded all reasonable limits, which is why such a lamp is doomed in advance. The device lives up to its name - the "brand" that gave birth to this lamp is called ... Long Hui ... Long, therefore, "hello" to you. From China...

Next, we take the LED analogue of the popular baseless five-watt car light bulb of the W5W size. The W5W LED lamp has a package, packed in 2 pieces in a blister, on which there is a brand of a certain Russian distributor, but, in fact, it is as cross-eyed and outbred as the Long Hui socket ...
For decent brands like Osram or Philips, the LED equivalent of a 5-watt W5W incandescent lamp consumes 1 watt, which corresponds to a current of about 0.07 amperes. The Chinese LED analogue W5W, as we see, “eats” much more - 0.26 amperes (about 3.5 watts) and also quickly warms up to painful sensations in the palm, while the operating temperature of such diodes should not exceed 45-50 degrees. ..
Conclusion: the lamp is conditionally suitable for short-term operation (say, in a trunk light), but in a long-term mode (say, in parking lights), it is also not a tenant ...

Another lamp-analog W5W. The lamp is completely outbred - even in comparison with the previous ones, because it is sold without packaging - "by weight". Its brightness is lower than the previous one, but the mode of operation is therefore more correct. After applying a voltage of 14.2 volts to the lamp, it consumes a current of 0.14 amperes - the lamp is warm, but not burning, which indicates an almost correct operation of the diodes.

The next "client" is a flat lamp of the C5W standard. We turn it on, we look - the lamp is not too bright, but it consumes less watts and heats up quite moderately. Must live long.

Well, in the end - light bulbs made in the format of bolts for installation in a bumper. Tin as it is ... The only ones, "thanks" to which the author managed to get a real palm burn - albeit mild ... They consume only 0.2 amperes, but due to the aluminum case they heat up from the outside to complete amazement. Without looking, taking the light bulb in his hand after burning for several minutes, he was forced to drop it with swearing and screeching!

A preliminary, intermediate conclusion looks like this - by inserting LED bulbs in their cars instead of classic ones, car owners, satisfied with their brightness and white light, close ceiling lamps, headlights and other lamps without knowing that at a voltage of 14.2 volts, the lamps warm up to an emergency temperature …
conclusions
In the end, I would like to voice clear and comprehensive recommendations for the selection of high-quality lamps ... But I do not undertake to do this for this reason. Take, for example, the notorious W5W light bulb - a five-watt, baseless, universally used in most cars. A classic W5W incandescent lamp from a good brand costs 20-30 rubles. Its unnamed Chinese LED counterpart already costs about 100 rubles - and although it shines brighter and consumes less energy, it is a lottery in terms of reliability. It can work for a long time if the Chinese did not go too far with brightness and current consumption, or it can “lean back” in a month or two. Accordingly, the LED W5W of a good brand, such as Osram or Philips already mentioned, will certainly work happily ever after, but at the same time it costs 500-800 rubles per pair, which I personally see beyond good and evil.

Actually, to advise the sacramental “buy a brand!” against the background of the foregoing, it is difficult, because the price gap between a high-quality incandescent lamp and an unnamed “diode”, not to mention the eminent “diode” ... 30 rubles for a true “classic” with a spiral versus 100 rubles for a diode lottery without a guarantee. Or even 30 against 250-300 for a European-made “diode”... One light bulb is still back and forth, but if you want to change a few pieces, then common sense already hints at the unproductiveness of such tuning, especially against the backdrop of a crisis .. .
Let's try to get to the conclusions that are constructive and understandable to the layman on the other hand - how to choose from the abundance of inexpensive unnamed Chinese LED bulbs so that it lasts a long time? Theoretically, this can be done, but in practice ... To come to the right conclusions, you need a too complicated procedure plus the skills of a radio amateur ... Pick up a light bulb, visually study the diodes, identify their breed, remember what current this type of diode consumes, count their number and calculate the approximate current consumption of the entire light bulb. After that, apply power to the lamp through an ammeter and determine whether the current consumed is close to the nominal or too high ... Nonsense?! Rave...
Another option is to buy a cheap LED lamp and independently build it into it or solder a selected resistor into the gap of the wire suitable for the cartridge, reducing the exorbitant brightness and temperature of the diodes. But here again, electrical skills and fuss are required, which will not suit everyone ...
So it seems that the circle is closed... If the above options do not suit you, then either we buy an expensive European brand, or we experiment with outbred light bulbs, changing them one by one and waiting for luck, or we don’t interfere in the design of the car at all and ... waiting for cheaper LED-devices!
If you encounter the problem that the LED lamp is on when the switch is off, do not be surprised. This indicates that current is flowing through the LEDs. The brightness of the glow depends only on its strength.
On the one hand, this phenomenon has a positive side, if the lighting is in the toilet or corridor can be used as a night light. What if it's in the bedroom? It is possible that the light does not smolder, but flashes periodically.
There may be several reasons for this phenomenon:
- Use of illuminated switches;
- wiring faults;
- features of the power supply.
The most common cause of a lamp glowing after being switched off is illuminated switches.

Inside such a switch is an LED with a current-limiting resistor. The LED lamp glows dimly when the light is turned off, because even when the main contact is turned off, voltage continues to pass through them.
Why does the LED lamp burn at full heat, and not at full power? Due to the limiting resistor, the current flowing through the electrical circuit is extremely small and insufficient to light an electric incandescent lamp or ignite fluorescent ones.
The power consumption of LEDs is ten times lower than that of an ordinary incandescent lamp. But even a small current flowing through the backlight diode is sufficient for a weak glow of the LEDs in the lamp.
There are two lighting options. Either the LED lamp burns continuously after turning off, which means that sufficient current flows through the LED backlight of the switch, or the light flashes periodically. This usually happens if the current flowing through the circuit is too low for a constant glow, but it recharges the smoothing capacitor in the power circuit circuit.
When sufficient voltage gradually accumulates on the capacitor, the stabilizer microcircuit is triggered and the lamp flashes for a moment. With such a flashing, it is necessary to unambiguously fight, wherever the lamp is.
In this mode of operation, the resource of the components of the power board will be significantly reduced, since even the number of operation cycles for a microcircuit is not infinite.
There are several ways to eliminate the situation when the LED light is on when the switch is off.
The easiest is to remove from the backlight switch. To do this, we disassemble the case and unscrew or bite off with wire cutters the wire going to the resistor and the LED. You can replace the switch with another one, but without such a useful function.
Another option would be to solder a shunt resistor in parallel with the lamp. According to the parameters, it should be designed for 2-4 W and have a resistance of not more than 50 kOhm. Then the current will flow through it, and not through the power driver of the lamp itself.
You can buy such a resistor at any radio store. Installing a resistor is not difficult. It is enough to remove the cover and fix the resistance legs in the terminal block for connecting the network wires.

If you are not particularly friendly with electricians and are afraid to “get into” the wiring yourself, another way to “fight” with illuminated switches can be to install an ordinary incandescent lamp in the chandelier. When turned off, its spiral will act as a shunt resistor. But this method is possible only if the chandelier has several cartridges.
Wiring faults
Why does the LED lamp glow after being turned off even if the illuminated button is not used?
Perhaps, during the installation of the electrical wiring, an error was initially made and zero is supplied to the switch instead of the phase, then after the switch is turned off, the wiring still remains “under phase”.
Such a situation must be immediately eliminated, since even with a planned replacement of the lamp, a sensitive electric shock can be received. Any minimal contact with the "ground" in this situation will cause a weak glow of the LEDs.
Features of the power scheme
In order to increase the brightness of the glow and minimize the pulsation of lighting, high-capacity capacitors can be installed in the power driver circuit. Even when the power is turned off, it still has enough charge to light up the LEDs, but it only lasts for a few seconds.
Content:Each manufacturer of LED lamps advertises its products as the highest quality and most durable. Such advertising is quite reasonable, since semiconductors consume a very small amount of current. As a result, the wear of LED lamps is significantly reduced during operation, and the use of such lamps becomes very profitable from an economic point of view, despite the relatively high price. Therefore, their failure becomes completely unexpected, and consumers have a completely logical question why LED lamps burn out.
As practice shows, it can be not only in the quality and parameters of the supply voltage. Lighting devices of this type often burn out for other reasons.
Wiring faults and defects
It should be noted right away that not a single electrical engineer will be able to determine the cause of the failure of the LED lamp only by describing the situation. In such cases, a mandatory visual inspection and advanced diagnostics are required.
One of the most likely reasons is the unsatisfactory condition of the wires in the electrical network. The characteristic signs of such a state are considered to be such a state in which the LED lamps in the apartment regularly burn out in one area, depending on the current power supply scheme. Therefore, before assuming a malfunction of the lamp itself, you need to carefully check all the lines. At the same time, it is recommended to perform an audit and preventive maintenance of the network.
First of all, the junction box is opened and the quality of all connections is checked. If there are twisted wires, especially, they must be removed, and instead of them, use special adapters, terminal blocks, mini-blocks and other devices. With their low cost, they are effective and in the future will provide protection against sparking, wire burning, insulation failure and other troubles that can cause LED lamps to burn out.
Checking the chandelier, identifying defects
If the wires were in good condition as a result of the check, you should check why the LED bulbs in the chandelier burn out. It is possible that the reason lies precisely in the unsatisfactory technical condition of the lamp. Since LED bulbs are highly sensitive to voltage drops, you must first check the quality of the connection of the chandelier to the wires of the home network.

After that, you need to check the lamp itself. The device and electrical circuits of most chandeliers are quite simple, which makes it easy to understand the problem and identify a possible malfunction. At the very beginning of the revision, it is recommended to check the contacts located in . They should not only be inspected, but also cleaned. Particular attention should be paid to the central contact, commonly called the tongue. If necessary, it is bent up, which significantly increases the reliability of the connection between the contacts and the light bulb.
Next, you should check how securely the wires are fixed at the connection points, especially in the cartridges. Insufficient fastening screws can cause sparking and burning. If ordinary incandescent lamps can withstand such overloads, then for LED bulbs such malfunctions turn out to be extremely dangerous. It has been established that burnt contacts change the resistance in these places, as a result, the current becomes unstable and prevents LED devices from functioning normally.
Poor quality LED bulbs
If during the checks no external negative factors were found, it is highly likely that the LED lamp burned out due to the poor quality of the product itself. This is especially true for Chinese-made products, in the electrical circuits of which there are no special devices - the so-called drivers. It is the drivers that protect semiconductor elements from voltage surges.

As a rule, there are no drivers in the budget versions of LED lamps, and instead of them a ballast is installed, which is absolutely useless during switching on and off, when the magnitude of the current surges becomes maximum.
During the purchase of light bulbs, they are checked at the stand. At this point, they shine with a good even light. However, in practice, many of them do not withstand loads and burn out. Due to wiring defects, twisting, sparking and other malfunctions, low-quality LED bulbs fail the fastest, while for good, proven lamps this is not at all critical.
One of the reasons is the voltage converter
Many high-quality LED lamps manufactured by well-known companies are equipped with fairly complex electronic circuits. The main function of these devices is to convert the alternating mains voltage into a constant voltage, the value of which is required for this type of LED. In addition, they qualitatively smooth out the resulting ripples.

A standard board usually consists of 1 or 2 chips and other elements. This design significantly increases the life of the lamps, but at the same time increases their cost. Therefore, in order to increase sales of products, unscrupulous manufacturers replace normal complex schemes with the so-called ballast, which was already mentioned earlier. In this regard, many consumers in the process of operation have a natural question why LED bulbs burn out quickly.
The main reason is current surges, which cannot be equalized with a simple ballast. As a result, the structure of the semiconductor is broken, the luminous layer - the phosphor - becomes inoperable. Therefore, it is recommended to buy products only from well-known manufacturers, which are distinguished by reliability and high quality.

