Shrink films and tubing became widely available about a decade ago. Initially, they were positioned as an alternative to PVC electrical tape used in electrical work. Later, another application was found for this material. This collection contains information on various types of heat shrinkage, its main properties and technical characteristics, marking methods and methods of use.
What is heat shrink tubing and its purpose
This term refers to a tube made of a special heat-shrinkable material (usually thermopolymers). Such a product can change its size under the influence of a certain temperature, the source of which can be hot water, air, or an open flame.
A characteristic feature of such tubes is a high transverse compression ratio relative to the longitudinal one. That is, the tube can reduce its diameter several times (as a rule, from 2 to 6), while its length will decrease by no more than 20% (for high-quality products, 7-10%). This effect is clearly demonstrated below.
An example of a change in the diameter of a heat shrinkable tube (hereinafter HERE) under the influence of temperatureThe figure shows a cambric, one part of which has undergone heat treatment (B), the second, which has not been heated, retained its original diameter (A).
Note that with a decrease in the diameter, the thickness of the walls of the product increases, which increases its electrical insulation characteristics.
Having dealt with the definition, let's move on to the purpose, that is, the sphere of using heat shrinkable materials. The main directions are as follows:
Views
The classification of products in this group is made according to the method of manufacture and the materials used for this. Depending on this, the following types of HERE are distinguished:

HERE is also usually classified according to the principle of installation, depending on this, the following types of heat shrinkage are distinguished:
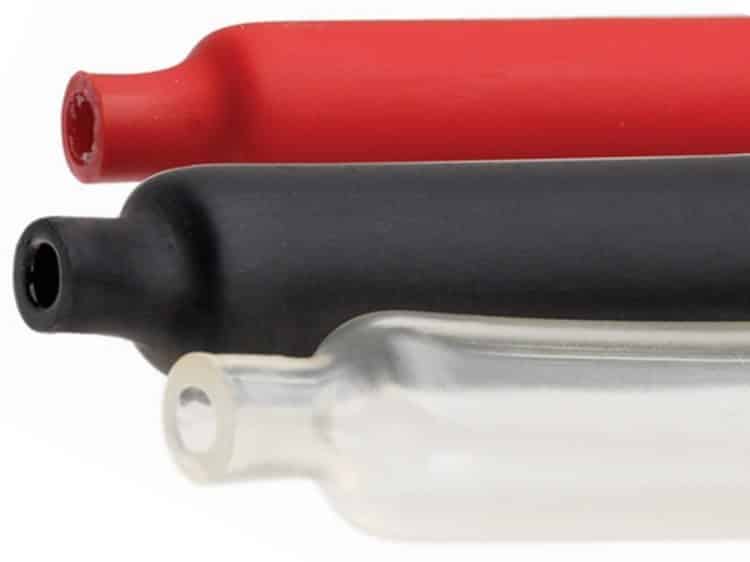

In addition, HERE is distinguished by wall thickness, they can be:
- thin-walled;
- middle-wall;
- thick-walled.
Also, manufacturers produce special types of HERE with certain additional properties. An example is products with increased electrical density (up to 1000 V), fluorescent additives, corrugated surface, etc.
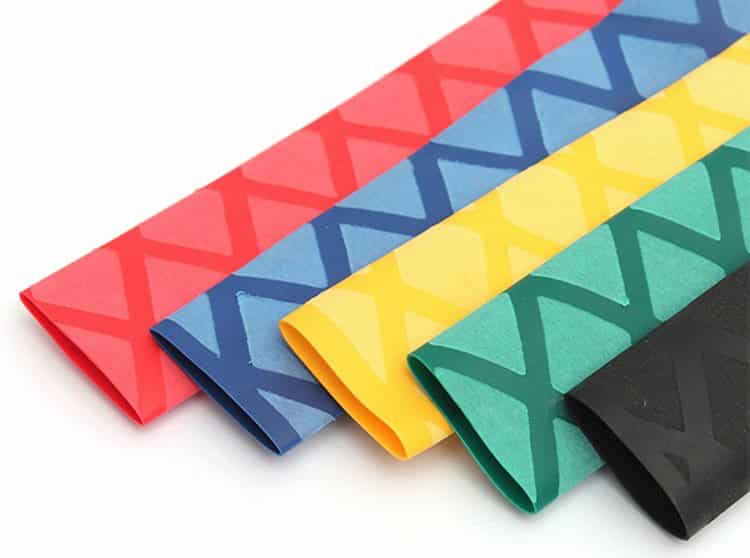

Properties and specifications
The main characteristic of HERE is the shrinkage coefficient, it can be from 200% to 600%. Accordingly, an important parameter is the diameter of the product before and after heat treatment. The technical characteristics also indicate resistance to a particular operating environment. Depending on this, the product may be:
- oil resistant;
- chemically inert;
- high-voltage (insulation can withstand voltages up to 1000 V);
- petrol resistant;
- light stabilized, not exposed to solar radiation, in particular UV;
- heat-resistant (non-combustible).
Also important characteristics are the temperature of shrinkage and working range.
As for the shape HERE, it can be flattened, oval and round. This does not affect the installation in any way, but is made for easy transportation. As a rule, thin-walled products are delivered in a bay, and for this it is more convenient to give a flattened and oval shape.
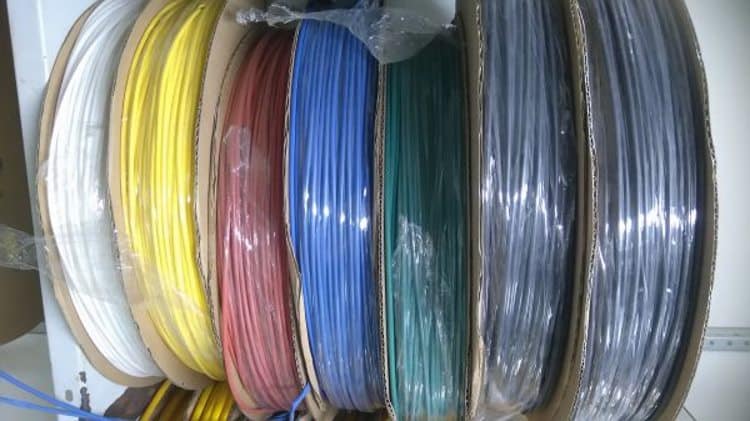

Glued and thick-walled products are transported pre-cut to prevent breakage.
Heat Shrink Tubing Marking
In most cases, the marking indicates the main parameters HERE, namely: diameters before and after shrinkage.

As a rule, these parameters are specified with a fraction, for example: "4.80 / 2.40 mm". It happens that the indication of diameters in inches is found, for the most part on products made in the USA and Europe. But you shouldn't trust this too much, counterfeit products can also have similar markings.
Some manufacturers indicate the original diameter and shrinkage ratio on the tubes, for example: "20 mm 3: 1".
Size range of heat shrinkable tubes
The range of products (in our case, the size range) depends on manufacturers and suppliers. You can get full information on this issue on the official websites of manufacturers or their dealers. As an example, we give information on the size range HERE®.
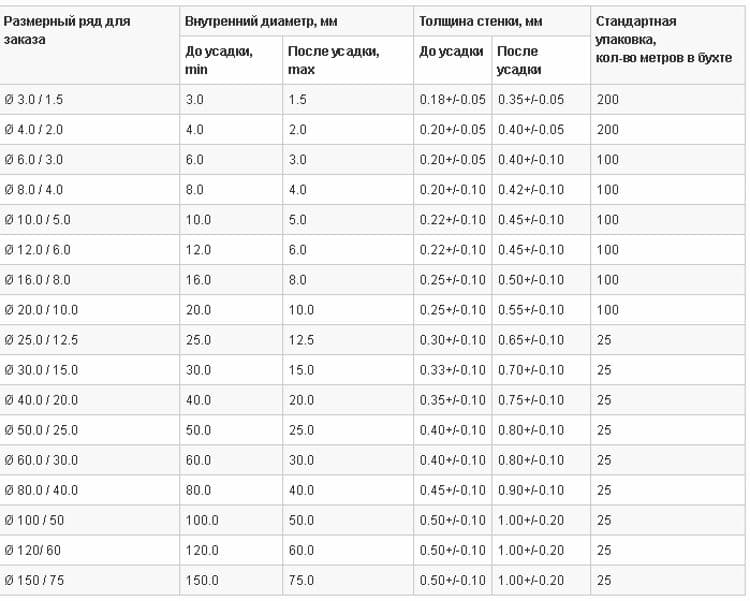 Table: available sizes from the manufacturer HERE
Table: available sizes from the manufacturer HERE Heat Shrink Tubing Selection
First of all, you need to decide on the operating conditions, then choose HERE with the appropriate characteristics. For example, if contact with fuels and lubricants is possible, then the product must be oil and petrol resistant. If it is necessary to ensure reliable insulation of the high-voltage cable wires, a tube is selected with protection at the junction up to 1000 V.
Next comes an important point - the selection of the diameter HERE. In this case, the “-10 + 20” principle should be used. It is as follows: the minimum shrinkage should be at least 10% of the original diameter and not more than 20% of the specified shrinkage parameter. An illustrative example of how this principle works is presented below.
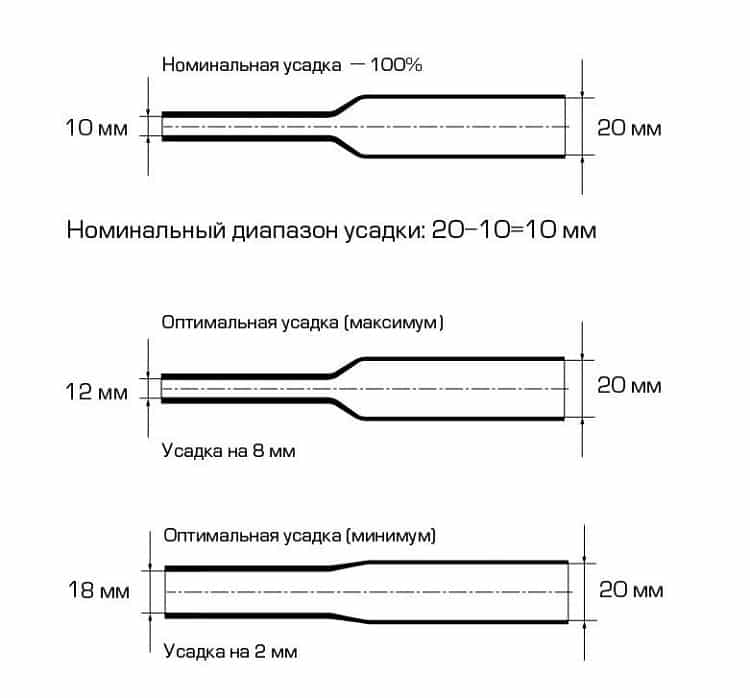
When choosing the length, it should be borne in mind that HERE gives longitudinal shrinkage. In low-quality products of the Land of the Rising Sun, it can be up to 20%. In branded kits, as a rule, the longitudinal compression does not exceed 5-7%.
How to use?
It is advisable to have specialized equipment for this process - a hot air gun or a thermal gun. You can set the required shrinkage temperature on them, which greatly simplifies the process. If it is not possible to use special equipment, you can heat the tube with an open flame (lighter or match) or place it in boiling water.
We will tell you in detail the algorithm of actions:
- It is recommended that thick or large sections HERE be heated to half the nominal temperature required for shrinkage before the process. The same goes for wide elastic bands. It is not necessary to preheat thin-walled products or small-diameter tubes.
- The required length is carefully cut off HERE. This can be done with ordinary scissors. Make sure that there are no tears or burrs, as tears can occur during the shrinking process.
- Next, the tube must be slightly stretched, and then pulled to the selected place. It is also necessary to put on HERE carefully so as not to damage the integrity of the surface.
- Heating is carried out in accordance with the indicated temperature. Exceeding it can lead to surface deformation. The hot air flow must be directed from one edge to the other or from the center to the edges.
- Upon completion of heating, it is necessary to allow the tube to cool down. After that, the procedure is considered complete.
As you can see, using HERE is quite simple, the main thing is to produce uniform heating and not exceed the permissible temperature. If the heat shrink tubing breaks or becomes deformed during installation, it must be removed and replaced.
Read the articles in the topic on the site:

