The life of indoor plants depends not only on proper care and watering, but also to a large extent on proper lighting. But if there is plenty of light in summer, then what to do in the autumn-winter period, when the sky is covered with clouds, and the daylight hours are incredibly short.
Plants need light to carry out the process of photosynthesis, due to which substances are formed in the plant body that serve as its building material. Naturally, different types of plants process photosynthesis in different ways, which is why they require different amounts of light. Generally speaking, all ornamental flowering plants need more light than ornamental foliage plants. Light-demanding plants include all types of plants from hot countries that are accustomed to a large amount of light throughout the year.
In addition, plants should be distinguished not only by how much light they need, but also how bright it should be. Some plants prefer direct sunlight, others prefer soft diffused light, and still others like partial shade. The minimum recommended illumination at which plants normally absorb carbon dioxide and other substances is 1000 lux, while for the full development of most plants, illumination is required at least 300-4000 lux, but for plants demanding light 10000-12000 or more lux.
If you do not have a special device for measuring lighting at home - a luxmeter, you can try to determine whether the plants have enough light for the eye. The following signs may indicate a lack of illumination:
- Plants develop very slowly, stem and leaves are thin and weak
- New buds practically do not form and have a pale color, and after formation they disappear
- The leaves of the plant acquire a uniform color, sometimes they can turn yellow and fall off.

What lamps to use for lighting
Selecting the right lamp is essential to arranging the right lighting for your plants. For example, many people believe that an ordinary incandescent lamp with a tungsten filament can provide enough light to plants. In fact, incandescent lamps are able to convert only 5% of the electrical energy received into visible light, converting the remaining energy into infrared (thermal) radiation, which causes plants to overheat and dry out. In addition to all of the above, the spectrum of an incandescent lamp is mostly red, while plants need both red and blue, which slows down the development of plants.
More suitable lamps would be modern LED and energy-saving lamps that emit a sufficient amount of light, but the spectrum of light emitted by them is also of little use for lighting plants.
The most appropriate in this case would be daylight fluorescent lamps
, providing cool daylight or special high pressure sodium lamps, which are often used in the late stages of maturation and growth of plants. Lamps of these types have an emission spectrum consisting of red and blue colors. In addition, they are economical and have a long service life.
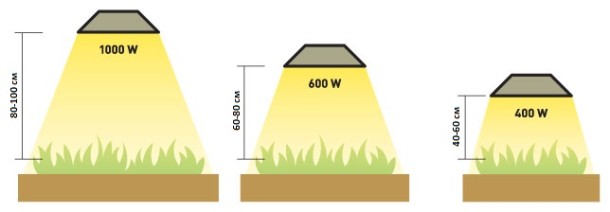
In order for the plants not to get burned, it is recommended to install lighting devices at a distance of at least 30-50 centimeters from the illuminated plants. It is also important to remember that plants are characterized by phototropism - a change in the direction of plant growth depending on the direction of the incident light. If you place lighting on the side of your plants, they will turn their leaves towards the light and lose their natural shape, so it is recommended to place the lighting directly on our plants.

