The means of protection against leaks is a special equipment protection device or abbreviated. The device triggers the protection, prevents the leakage current from reaching a dangerous value and is the main means of protecting a person from electric shock.
For comprehensive protection of equipment, they are used together with. According to the currently accepted standards, RCDs are mandatory for installation in the power supply network, regardless of the purpose of these networks.
How does it work
The RCD works on the principle of comparing two currents that flow through a protective device. In this case, the current at the input of the device and the current at the output are compared. If these values differ, then a protective operation of the device occurs.
To check the operability of the device, the test button is used, when pressed, a trial operation occurs, by which you can determine the protection status.
How to choose and not make a mistake
Regardless of the purpose, the devices are selected according to the following parameters:
- load capacity. For the device, the magnitude of the current for which its power contacts are designed is important. At face value, they are most often used at 16A, 25A, 32A, 40A, 63A, 80A.
- Leak detection method. According to the type of leakage detection, they are divided into electronic, the leakage of which is determined by an electronic key, and electromagnetic, the leakage value of which is taken from the magnetic core. Electronic ones are more affordable, but have drawbacks in operation in the form of failure when one of the phases fails.
- Sensitivity to leakage current. Sensitivity determines the ability of the device to operate. The most sensitive devices for 10 mA leakage current. But their use is limited by the number of consumers due to possible false alarms and the presence of natural leakage currents.
- Circuit current type. According to the type of currents, they are divided into those operating from alternating current and pulsating current.
According to the number of connected phases, they are divided into two-pole and four-pole. Single-pole for a 220 V network, three-pole for 380 V. In houses and private households, due to the use of a single-phase network, single-pole RCDs are used.
To select a protection device, it is necessary to determine its purpose. According to the purpose, it can be divided into the following types:
- household- these are single-pole RCDs of low sensitivity with a load current of not more than 50 A. Such requirements are due to the large number of household appliances and the large natural leakage points associated with this. Very sensitive ones will constantly false-trigger. A load current of 50 A is determined by the parameters of electricity meters installed in residential premises, not exceeding this rating.
- For industrial applications- sensitive four-pole RCDs with high current ratings. These requirements are due to the high current consumption of industrial equipment, the use of a three-phase network and increased requirements for its protection due to its increased danger and high cost.
- Specialized. Fire-fighting type B are specialized. They are highly sensitive not only to AC leakage, but also to slight DC ripples.
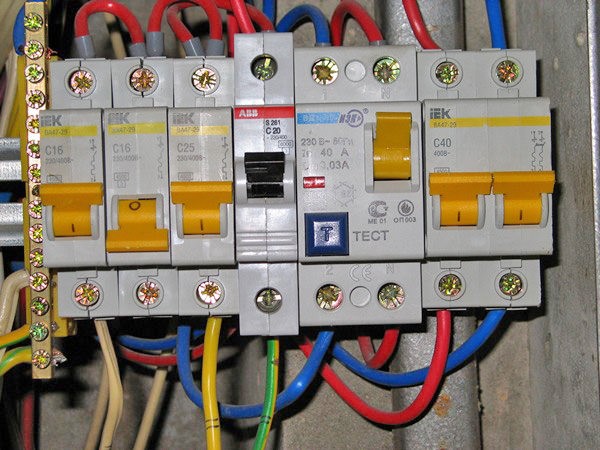
Electronic RCDs are more affordable, but have drawbacks in operation in the form of failure when one of the phases fails
Connection rules
When connecting an RCD, you must follow the following rules:
- The device must always be installed after circuit breakers, since it is not protected from exceeding the current maximum values;
- The circuit breakers in the circuit must be of a smaller rating, since the fuse response time is long and the current may be sufficient to disable it;
- Protected RCD lines must be connected to it otherwise the protection will not work.
- Connect the device only according to the manufacturer's instructions., for example, it is strictly forbidden to change the input and output of the device. This will surely cause a malfunction and its further unusability.
- Check the reliability of all connections and exclude possible sparking which in turn can cause a fire.
- All connecting conductors must be well insulated from each other, must not have damage to the insulation, traces of oxidation. When corrosion centers appear, in an environment with high humidity, leakage through oxides will cause constant protection trips. This can lead to serious malfunctions in connected consumers;
- Housings of installed elements must not have visible damage or defects.
![]()
When corrosion centers appear, in an environment with high humidity, leakage through oxides will cause constant protection trips.
Connection order
It is important to remember that all work with RCDs in the electrical panel is carried out with the power off. The installation process can be divided into 5 steps:
- switchboard preparation;
- marking of the shield for the installation of all elements of the electrical circuit;
- installation of an electricity meter;
- installation of automatic switches;
- installation of zero;
- RCD installation;
- connection of electricity consumers to the RCD network.
Mistakes often occur during installation. The most common of them:
- Incorrectly selected element types. The grossest mistake - the rating of the input circuit breakers exceeds the rating of the RCD. The scheme in this form not only poorly protects the network, causes false protection trips, but is itself a potential source of an accident;
- Installation of the device in front of the counter. Due to the presence of a rather large magnetic circuit in the RCD, the meter readings will not be correct and the representative of the power supply company will not accept such a design into operation;
- Wiring diagram mismatch neutral poles;
- Inclusion of neutrals in parallel;
- Erroneous connection protective earth to neutral.
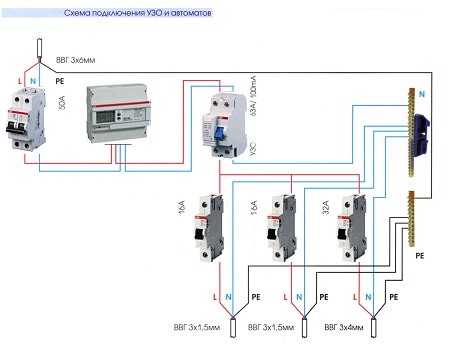
Wiring diagram "introductory machine"
Currently, as a rule, three-wire house networks with protective earth are used.
The central circuit breaker is installed first in the circuit. Behind it, the electricity meter is turned on and only after it comes the RCD. According to well-known rules, the RCD rating exceeds the ratings of automatic load breakers by an order of magnitude. With such a scheme, it is important to ensure the correct connection of the neutral and phase wires.
- the presence of only one expensive RCD;
- a small amount of workspace that is occupied by one device.
The disadvantage of the scheme is:
- difficulties in finding faulty wiring;
- the difficulty of selecting parameters for existing consumers.
The disadvantages of this scheme are eliminated by parallelizing consumer groups and installing an additional RCD.
![]()
Connection to a three-phase network with grounding according to the "separate machine" scheme
The electrical circuit of a large residential facility implies the presence of a variety of energy consumers. For appliances such as a powerful refrigerator, washing machine, oven, a separate RCD is required. This is necessary to protect a particular device and maintain the performance of others that are not related to it.
The safest switching circuit is a three-wire circuit with grounding, and using a selective four-pole RCD, it becomes possible to connect to a three-phase industrial network. With this scheme, protection against damage to the circuit insulation and from leakage is also provided.
Advantages of the "separate machine" scheme:
- the convenience of finding a leak in the circuit, since the circuit arms have individual devices.
- the ability to connect consumers of much higher power;
- this scheme provides the highest level of protection.
Disadvantages of the "separate machine" scheme:
- high price due to the large number of blocks;
- significant volume occupied by the scheme;
- the impossibility of building such a circuit without the presence of a three-phase power supply.
The power supply circuit from a single-phase source is practically equal in functionality to the previous circuit. In it, you can abandon the selective RCD and thereby reduce the cost, but the load capacity of this network will be much less.
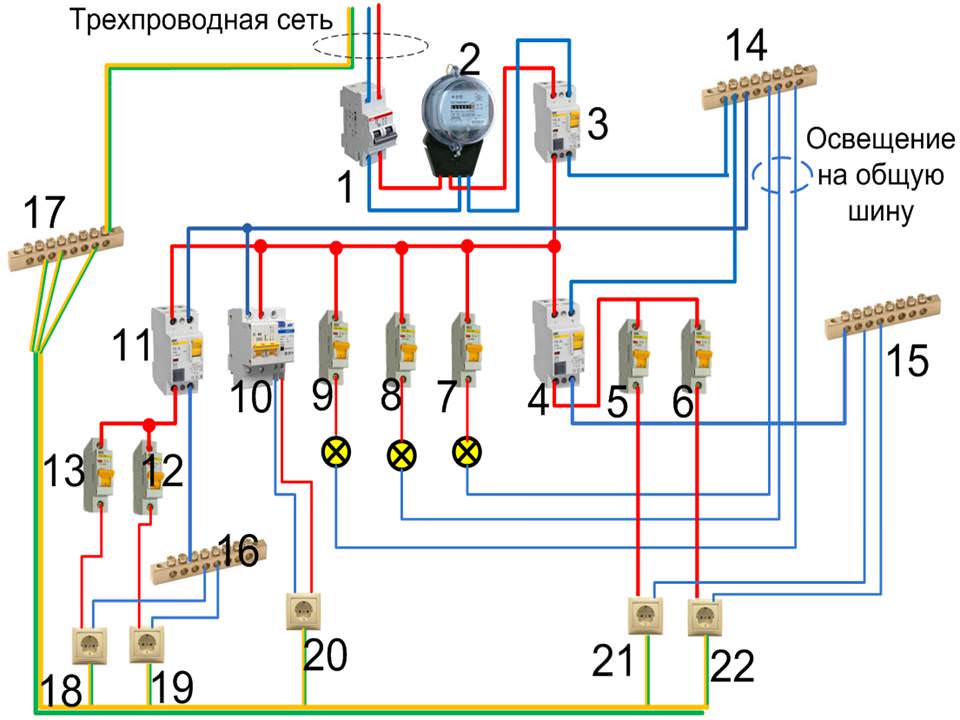
Scheme of connecting the RCD to a three-phase network
Connection diagram without protective earth
Not everywhere and not always the power supply networks are equipped with protective grounding. Often in private households built a long time ago, wiring is done without the possibility of grounding. In this case, the installation of an RCD is not only desirable, but also necessary for the safety of residents.
How will the device behave without grounding? In order for the RCD to perform its functions, the zero bus must be connected to the wire coming from the power input. In this case, the RCD will work as if on its own.
In the diagram, the letter N indicates the neutral wire. Since there is no ground in this circuit, it is incorrect to assign this name to another line.
In the light of the data reviewed, it can be said that protection should never be neglected. Despite some difficulties, even in a two-wire line, it is always possible to install a Residual Current Device. Don't skimp on security.
- The use of RCDs in the bathroom and bath is necessary. Due to high humidity, the conductor insulation does not last long. Lack of protection in the power circuit can be deadly.
- When using a two-wire switching circuit, in no case should a self-made grounding device be installed. Homemade grounding systems are not associated with third-party consumers. For this reason, no one knows which phase of the three will be on your neutral wire when the trunk line breaks.

