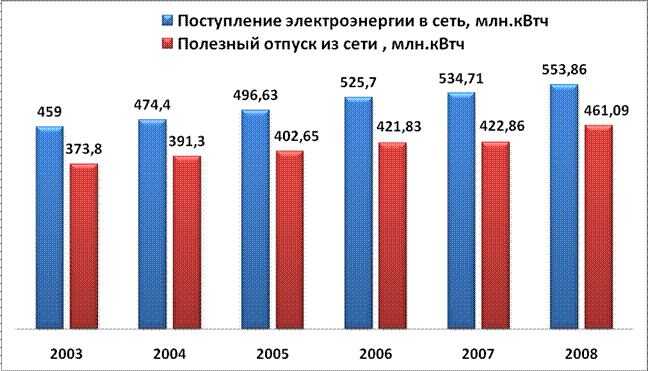
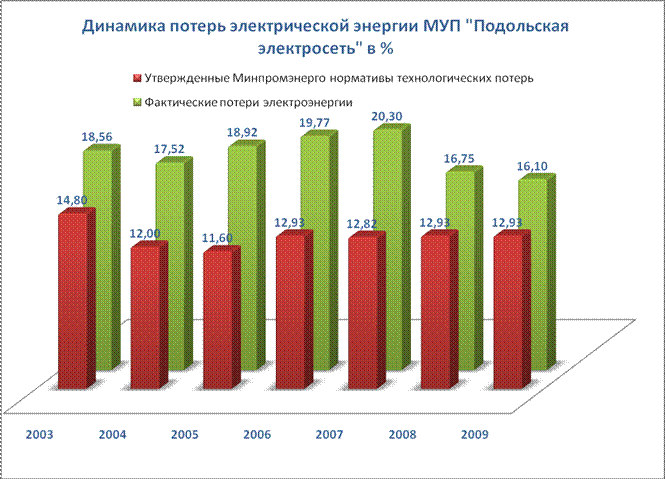
In electrical networks, there are large actual losses of electricity.
Of the total amount of losses, losses in power transformers of MUP "PES" are approximately 1.7%. Electricity losses in 6-10 kV transmission lines are about 4.0%. Electricity losses in 0.4 kV networks are 9-10%.
Analysis of the dynamics of absolute and relative losses of electricity in Russian networks, their modes of operation and load shows that there are practically no significant reasons for the growth of technical losses caused by the physical processes of transmission and distribution of electricity. The main reason for the losses is the increase in the commercial component.
The main reasons for technical losses are:
Deterioration of electrical equipment;
Use of outdated types of electrical equipment;
Inconsistency of the used electrical equipment with existing loads;
Suboptimal steady-state modes in distribution networks by levels
voltage and reactive power.
The main reasons for business losses are:
Inadmissible errors in electricity measurements (inconsistency of metering devices with accuracy classes, inconsistency of current transformers with existing loads, violation of the verification time and malfunctioning of energy metering devices);
The use of imperfect methods for calculating the amount of supplied electricity in the absence of metering devices;
Imperfection of methods for taking readings from metering devices and issuing receipts directly by subscribers of the household sector;
Non-contractual and unaccounted for electricity consumption (theft);
Distortion of volumes of electricity supply to consumers.
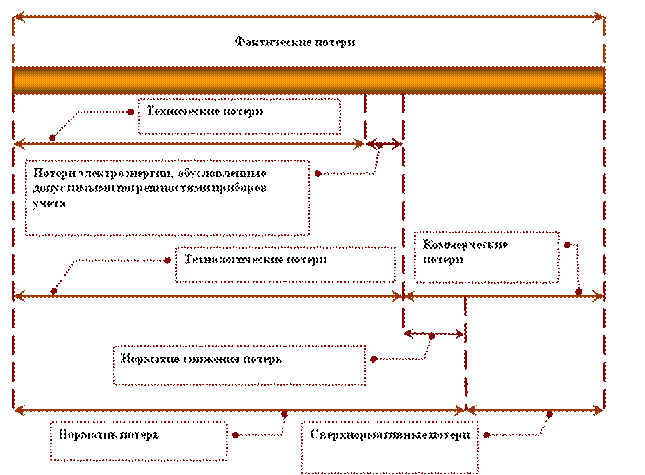
ACTUAL ELECTRICITY LOSSES
IN MUP "PODILSK ELECTROSET"
STRUCTURE OF ACTUAL ELECTRICITY LOSSES
 |
|
| |||||||||||
Technological losses of electricity (hereinafter referred to as TPE) during its transmission through TGO electric grids include technical losses in the lines and equipment of electrical networks caused by physical processes occurring during the transmission of electricity in accordance with the technical characteristics and operating modes of lines and equipment, taking into account the consumption electricity for auxiliary needs of substations and losses due to permissible errors of the electricity metering system. The volume (number) of technological losses of electricity in order to determine the standard of technological losses of electricity during its transmission through electric grids is calculated in accordance with the instructions for organizing work in the Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation to calculate and substantiate standards for technological losses of electricity during its transmission through electric networks, approved by order No. 000 dated 01.01.2001.
Methods for calculating standard losses of electrical energy
Basic concepts
![]() 1. Acceptance of electrical energy into the network
1. Acceptance of electrical energy into the network
2. Return of electrical energy from the network
4. Actual (reported) electricity losses in absolute units
6. Technical losses of electricity
9. The rate of technological losses of electricity in absolute units
11. Standard energy losses, absolute
Calculation of losses in electrical network equipment
ü Losses of electricity in the overhead line
ü Losses of electricity in the cable line
ü Losses of electricity in transformers (autotransformers)
ü Losses of electricity in current-limiting reactors
Conditionally constant power losses
Ü losses in steel of power transformers and autotransformers;
Ü losses in steel shunt reactors;
Ü corona losses in overhead lines 110 kV and above;
Ü losses in capacitor banks (BSC) and static thyristor compensators;
Ü losses in synchronous compensators (SC);
Ü losses in surge arresters;
Ü loss of electricity in direct connection meters;
Ü losses in measuring current and voltage transformers;
Ü insulation losses of cable lines;
Ü losses from leakage currents on insulators of overhead lines;
Ü losses in connecting wires and busbars of substations;
Ü electricity consumption for melting ice;
Ü consumption of electricity for auxiliary needs of substations, taking into account the losses in steel and copper of transformers for auxiliary needs, when accounting does not coincide with the boundary of balance sheet membership.
Variable energy losses
Ü load losses of electricity in transformers and autotransformers
Ü load losses of electricity in overhead and cable lines
Ü power losses in current-limiting reactors
Methods for calculating variable losses
Method of operational calculations of steady-state modes using data from operational dispatch complexes (OIC)
Method for calculating losses according to the calculated day (using operating data for a characteristic day)
Method for calculating losses based on average loads
Method for calculating losses in the mode of maximum network loads using the number of hours of maximum power losses
Estimated calculation methods
On-line settlement method
Electricity losses on a time interval in a three-winding transformer
Settlement day method
Electricity losses for the billing period
Graph Shape Factor
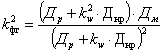 |
Average load method

