In electronics, many inventions of mankind have found their application. One of them is an intermediate relay. What is it, what is its purpose and how can it be characterized. How is an intermediate relay classified? What are the features that you need to consider when choosing?
What is an intermediate relay?
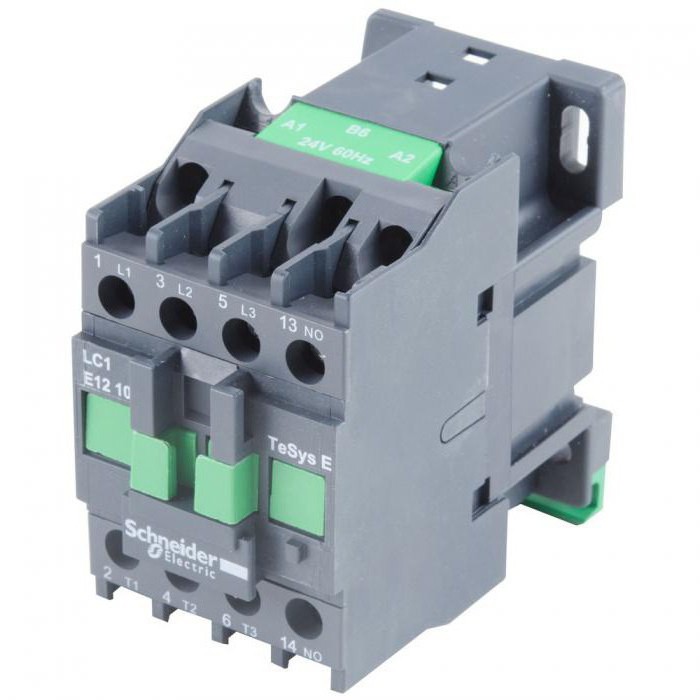
This term refers to electromagnetic relays that are used as auxiliary parts. They play, albeit not the main, but very important role in the construction of control schemes for various technological installations, machines and complexes. At the moment, manufacturers have provided a wide range of products and it is possible to choose the desired item, taking into account both the price and the list of tasks to be solved. If we simplify the schematic representation, then the intermediate relay is an electromagnetic coil with a core that is connected to alternating or direct current. When voltage appears, it attracts an armature, which closes the moving contacts with the fixed ones. This is due to the electromagnetic force.
During the supply of current, the groups of contacts are closed or opened. They, in turn, perform their functionality (include protection or alarm circuits and similar mechanisms). The power supply for the coil of the magnetic starter of the electric motor can also close or open. Use cases, without exaggeration, the mass. How much current does the intermediate relay have? 10A is how many amps most samples are calculated for. But this is not the only energy characteristic. Under what voltage are manufactured products produced? How long can an intermediate relay withstand? 220V - this is the voltage under which most of these devices are manufactured. But these are not all the parameters that you need to pay attention to. In addition, for effective operation, it is necessary that the intermediate relay work effectively in the conditions that exist. How to choose a device, taking into account the nuances, will be discussed closer to the end of the article.
Purpose
 In what cases can an intermediate relay be used? I remind you that this is an auxiliary device, and it is used in such situations:
In what cases can an intermediate relay be used? I remind you that this is an auxiliary device, and it is used in such situations:
- It is necessary to open or close a certain number of circuits at the same time. Contacts are being multiplied. Example: one of them trips the circuit breaker, and the other activates an alarm in the alarm system.
- A powerful relay should be controlled that switches many circuits with high currents. For example, it is necessary to apply voltage to the switch actuator, which turns on the solenoid. The switching current in this case reaches a value of 63 amperes. It is difficult to do this using only one intermediate relay. Therefore, voltage is first applied to the coil, and with the help of its contacts it turns on a more powerful component. It also switches currents of high values.
- If it is necessary to create an artificial slowdown of actions, which relate to relay protection.
Intermediate relay connection
 But how to actually include this mechanism in the chain? Are there any methods? Yes! There are currently two options available:
But how to actually include this mechanism in the chain? Are there any methods? Yes! There are currently two options available:
- Shunt. The relay winding is switched on to the full mains voltage. Because of such loads, this method received a second name. So, the inclusion of an intermediate relay is also called a voltage winding.
- Serial. This type is implied when the relay winding is connected in series with the trip coil of the breaker actuator. This implementation process also has a second name. It is also called current winding.
Intermediate relays must be guaranteed to operate when there is a normal voltage of the auxiliary power supply. Moreover, it is envisaged that they will work even if there is an emergency voltage drop of 60-80%. Based on the design features, they can be made with one, two or three windings (the latter version is very rare).
Classification
 Many different types of intermediate relays have been developed. They can be classified based on their characteristics, what they are made of, what they live on. Here is the last typology and will be told:
Many different types of intermediate relays have been developed. They can be classified based on their characteristics, what they are made of, what they live on. Here is the last typology and will be told:
- With DC solenoid. The response time may vary. To do this, reduce the ratio of self-induction voltage relative to the applied and reduce the eddy currents. Such changes lead to an increase in the current consumption.
- With AC solenoid. Faster acting than the previous version. But they almost always consume more energy.
Selecting the required device
 On what basis should an intermediate relay be selected? The only right decision is the orientation by technical characteristics. More specifically:
On what basis should an intermediate relay be selected? The only right decision is the orientation by technical characteristics. More specifically:
- Supply voltage (in volts).
- Power consumption (in watts).
- Switching current (in amperes).
- Type and number of contacts.
- Continuously admissible current of contacts (in amperes).
- Type and number of contacts.
- Dimensions.
Also, do not forget about the conditions under which the intermediate relay will operate:
- Operating temperature range.
- industrial vibration.
- Increased explosiveness of the working environment.
- dust concentration.
- Air humidity.
And every requirement can be satisfied with a custom-made type of intermediate relay. When choosing elements for the system, remember that each of them introduces its own error into the protection circuit. You should also take into account the fact that the intermediate relay has a certain response time. As a result, the protection may work for a time interval that reaches a value of 0.1 seconds. The most operational mechanisms can boast an indicator of 0.02 s.
Prices
We talked about what an intermediate relay is. The price of this device varies greatly from the required technical characteristics and can range from 120 to 1500 rubles for new samples. Anything below this is either defective or low quality (may fail even on the day of purchase).

