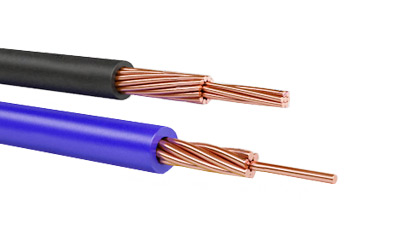
3 PV wire which has found wide application both in industry and at the household level. Ease of installation, a large selection of cross-sections, excellent physicochemical properties of insulation and durability have been recognized by electricians. Due to this, PV3 wire is used almost everywhere.
Explanation of the name and design features of PV3 wire
At the first stage of our acquaintance with this wire, let's figure out the decoding of its abbreviation, as well as the design features. Moreover, there are "pitfalls" here.
Explanation of the name PV3
And these "stones" are hidden in the decoding. The fact is that now such a wire as PV3 is not produced. Its name has changed somewhat. But let's talk about everything in order.
So:
- According to GOST 6323 - 79, the first letter in the abbreviation indicates that this conductor is a wire. The second letter indicates the insulation material. In our particular case, this is "B", which means vinyl or as it is also called polyvinyl chloride.
- The number 3 at the end indicates the flexibility class of the wire. There are 6 classes in total. And the lower the number, the less flexible the wire. That is, PV 1 3 wire is much less flexible than PV 3 3 wires.
- This was the case until 2010. But in 2010, a new standard GOST R 53768 - 2010 was introduced, which made drastic changes. According to it, the structure of the designation of brands of wires and cables has completely changed.
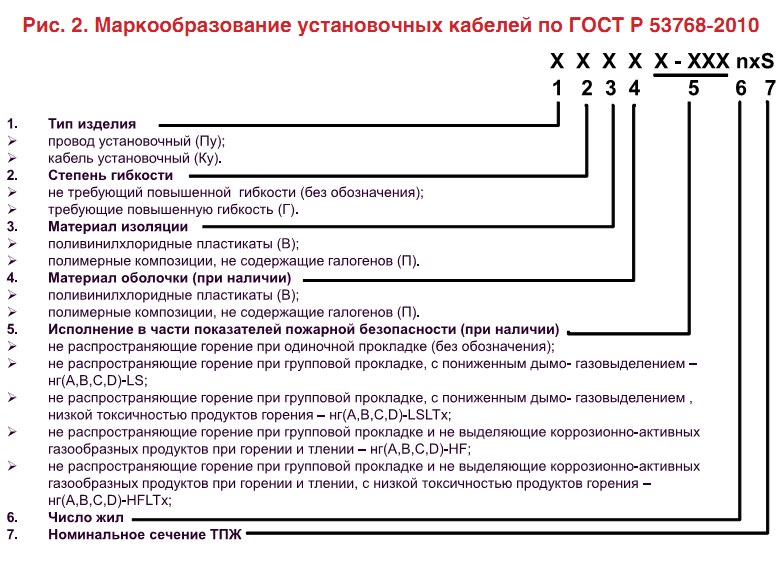
- Now our PV3 wire should be called PGV. Therefore, let's take a look at this abbreviation as well.
- Pu - denotes an installation wire. In general, now there are only two types of the first symbols Pu - wire and Ku - cable.
Note! Previously, less flexible wires were referred to as the installation wire. The more flexible ones belonged to the installation wires. Now all wires are attributed to installation, and their flexibility is indicated by the corresponding symbol.
- The "G" symbol means that the wire is flexible. If the wire is not flexible, then no symbols are indicated at all.
- The last character is "B". It, as before, means PVC insulation.
- In addition to these symbols, the modern abbreviation may contain information about the material of the shell, if any, and about the class of fire safety, if there is such protection.
- After that, the name of the wire usually contains numbers from 0.5 to 95. They indicate the cross-section of the wire.
Now let's look at the construction of the wire itself. As you can see in the video, PV3 wire is single-core. Copper wire is used as live parts.
|
|
In order for the wire to be flexible, each current-carrying conductor is made of several wires twisted together. So wires with a cross section from 0.5 to 35 mm 2 are made from at least 7 separate wires. The smaller the section of each individual wire, the higher the flexibility of the wire. So according to GOST 6323 - 79 for wire PV 3 of these cross-sections, wire of the 2nd, 3rd and 4th class of flexibility can be produced. |
|
|
The flexibility class can vary depending on the cross-section of each individual core. So, for example, for wires PV 3 3, a wire with a diameter of no more than 0.79 mm can be used. In this case, the wire will have a flexibility class 3. If a wire with a diameter of no more than 0.53 mm is used, then the characteristics of such a wire will allow it to be attributed to the 4th class of flexibility. |
| But for wires with a cross section of 50 - 95 mm 2, the cross section of each individual wire should be no more than the values specified in GOST 22483 - 77 for the third class. By the way, the number of these wires must be at least 16 pieces. |
|
|
|
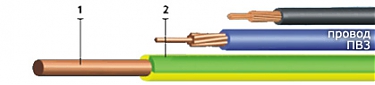
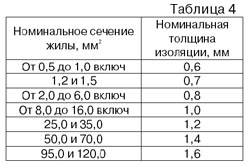
The next important element in the construction of a wire is insulation. But everything is quite simple here. Depending on the cross-section of the wire, its thickness is strictly specified and must correspond to the values given below. According to GOST 6323 - 79, the wire insulation can be two-layer. In this case, the thickness of the first layer must be at least 70% of the thickness of the entire insulation. |
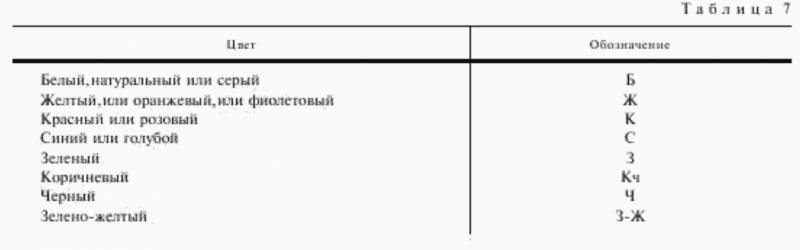 |
The last issue we will pay attention to is the color of the wire. The eight colors listed below are considered the main ones, but at the request of the customer, any color of the insulation surface can be performed. |
Note! When a two-color wire is painted on any section of insulation 15 mm long, the color ratio should be within 30 - 70%.
Mechanical and electrical parameters of PV3 wire
Now you can consider the main technical characteristics of PV3 wire. They can be divided into mechanical and electrical. And they should be considered separately.
Mechanical characteristics of PV3 wire
To the mechanical characteristics of the wire, we refer not only to its physical and chemical properties, but also durability, operating conditions, as well as resistance to aggressive media.
So:
- One of the main mechanical characteristics of any wire is the ability to bend it.... This is especially true for PV3, which is a flexible wire. The permissible bending angle directly depends on the diameter of the wire, therefore, everywhere it is indicated precisely based on this parameter.
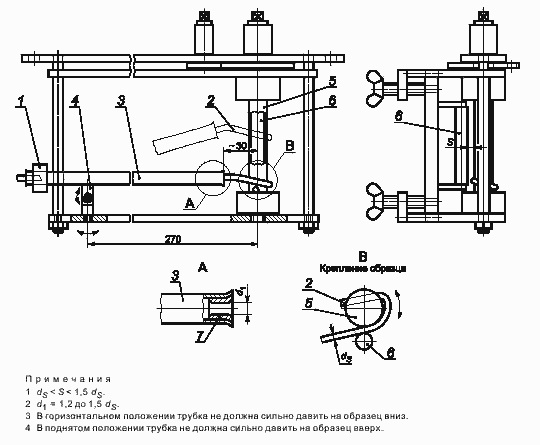
For PV3 wire, the permissible bending radius is at least ten of its outer diameters. This parameter is checked during commissioning and periodically during operation.
- The next important parameter is the operating temperature range of the wire. For PV3, it is - 50⁰C - + 70⁰C. It is important to note that the installation of the wire can only be carried out within the temperature range -15⁰С - + 35⁰С.
- Also, a fairly relevant parameter is the non-flammability of the cable.... At the same time, certain types of products may not only have a non-combustion-supporting class, but also belong to self-extinguishing wires. It is clear that the price for such a wire is higher.
- The service life of such a wire is 15 years.... Moreover, if the wire does not come into contact with aggressive media and does not have contact with the external environment, then its service life can be increased.
Electrical characteristics of PV3 wire
But since our wire is primarily a conductor of electric current, then of course the electrical parameters are very important for it. And when choosing a wire, they cannot be deprived of their attention.
So:
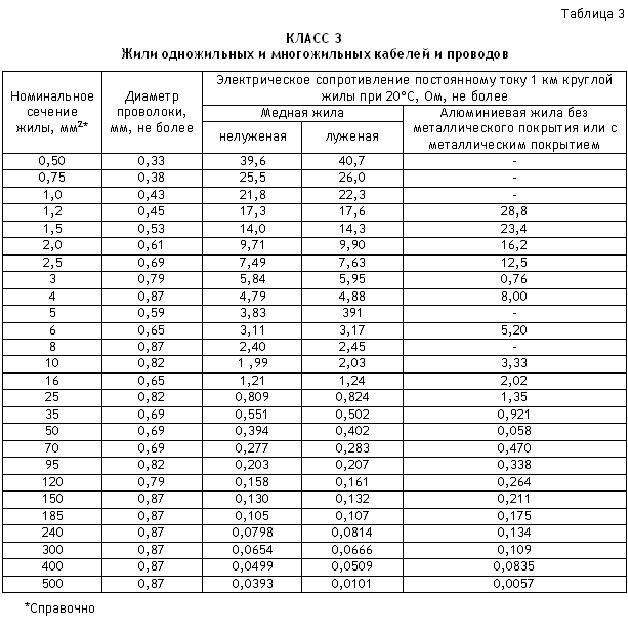
- One of the main electrical parameters of any wire is its resistance.... As you know, this parameter depends on the cross-section of the wire and on its temperature. Therefore, all measurements that you are quite capable of doing with your own hands must be brought to a temperature of 20 ° C.
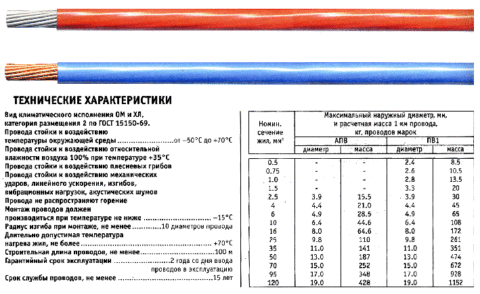
It is necessary to bring the measured results to a given temperature because it is for this temperature that GOST sets its requirements for wire resistance. These values are given for a wire 1 km long and are presented in the photo below.
- Another important electrical characteristic is the insulation resistance of the wire.... It must withstand the operating voltage for a long time. For this, the insulation is subjected to high-voltage tests.
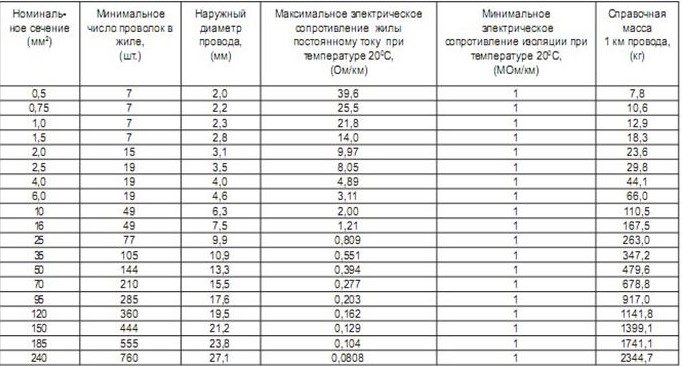
- Tests are carried out in accordance with GOST 23286... The wire is placed in a bath of water and left there for a day. After that, a test voltage of 2500V is applied to its veins. It is supplied within three hours after which the wire is considered to have passed the test.
How to choose the right wire PV3?
During acceptance and during operation, the wire must be tested. They are designed to determine its mechanical and electrical properties, as well as determine the possibility of its use in the future.
- So, when accepting a wire for operation, it must go through the following stages - checking the design and dimensions, checking the electrical resistance of current-carrying conductors, voltage testing, determining the insulation resistance, checking the marking and packaging, as well as checking the strength of the colors and markings.
- But the wire must pass an order of magnitude more periodic tests. These include high-voltage tests, determining the resistance of a live part, testing for bending and impact at a temperature of -15 ° C, determining the strength and elongation at break, tests for weight loss, thermal shock, thermal stability, low temperatures, elevated temperatures and non-propagation burning.
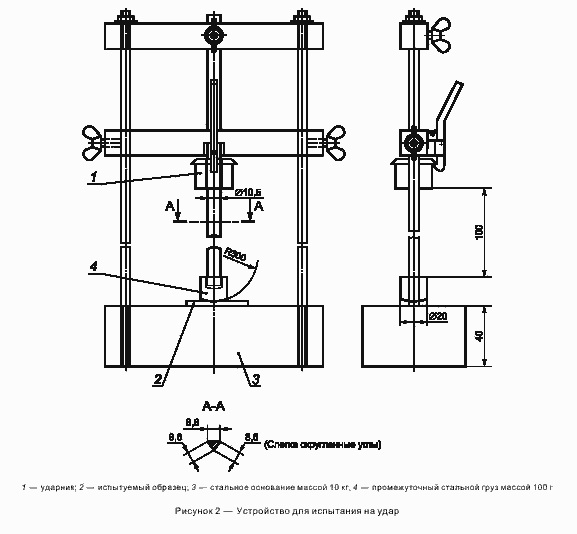
- As instructed by the instruction, all these tests should be carried out in accordance with GOST 44295, as well as a number of other regulations. And each of them has its own technical requirements. Therefore, only specialized organizations can carry out them.
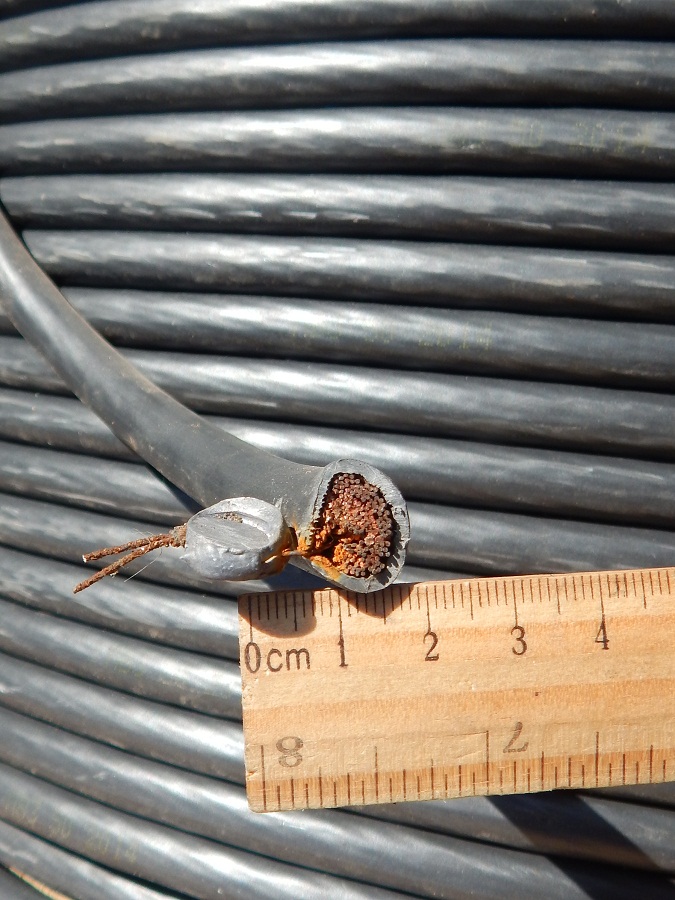

- When buying a wire, an ordinary consumer should pay attention to much simpler things. First of all, this is a check of the dimensions by the declared seller. In this case, it is sufficient to measure the diameter of the conductor using a vernier caliper.
- We can also easily measure the resistance of the current-carrying parts of the wire. To do this, you can use an ordinary multimeter and measure a piece of wire of a strictly defined length. In the future, it will be possible to bring these values to those specified in the GOST.
- Instead of testing the insulation, we can simply measure its thickness and at the same time check how easy it is to remove. To do this, we again need a caliper.

- And of course, you should make sure by the markings on the wire and on the coil that this is exactly the wire we need and that it is manufactured at the factory. After all, the manufacturer's tag must be on the bay. And the presence of markings on the wire every 50 - 55 cm is a good sign of compliance with GOSTs in the manufacture of this product.