The main part of homeowners deeply does not care what they have installed in the electrical box - a simple or differential automatic. Relying on electricians of dubious qualifications when developing a power grid project, such citizens risk getting problems in terms of electrical safety. Therefore, it makes sense to study the functional features and differences of units that protect not only the networks of the house, but also the health of the residents themselves.
What are the differences in the principle of operation of the residual current device and the difavtomat
We will not consider in detail the design and foundations of the functioning of these devices. However, the information provided will be enough to understand absolutely exactly what is installed in the shield and how safe it will be in the future. Of course, experienced electricians know such details thoroughly, but ordinary consumers will be interested. The topic is especially relevant in the implementation of the modernization of household electrical networks: repair of wiring, , installation of the shield.Outwardly, it is almost impossible to understand how an RCD differs from a differential current circuit breaker. They are similar, but their functions are different:
- Residual current device- comparing the amount of current suitable for the electrical consumer and coming from it, the device determines the level of leakage. When the difference in current values reaches life-threatening scales (on average, 30 mA), the protective device will disconnect the voltage. This not only saves a person from electrical injuries when touching damaged equipment, but also effectively prevents a fire when the conductors are heated in the event of a leak.
- Difautomat Is a unique design that combines an automatic machine and the already mentioned RCD. Thus, the differential circuit breaker protects the wiring from overloads and short circuits, as well as from the occurrence of current leaks.

In general, the residual current device and the principle of operation of its circuit protects against electric shock and wiring leaks, accompanied by fire. Many users believe that by installing this switch, they are completely protected. By no means, this is not so, unlike the difavtomat, it is not able to protect the network from overload and short circuits.
In simple terms, such a switching device monitors the presence of current leakage from the main consumers. When the insulation is damaged, the circuit will react and shut down the network. At the same time, the RCD has a number of disadvantages:
- When a number of powerful electrical consumers are switched on simultaneously, an overload is created, and the unit will not work.
- If you connect the phase and zero while the residual current device is operating, i.e. organize a large short circuit, then the device will also not turn off the network.
- When the "neutral" is disconnected, the element does not work, at this time there is voltage in the phase conductor, which is dangerous.
- The installation will not be able to operate when the mains voltage drops below the nominal. The electronic type of devices is completely dependent on the availability of supply energy, their mechanism operates from a controlled network or an external power supply.
conclusions
The listed points are quite enough to understand how an RCD differs from a differential circuit breaker, without delving into the specifics of their design. Summing up, it is important to note that the residual current device is not able to protect the network from short circuit or overload. Therefore, it is always included in the circuit in series with a conventional automatic machine, so that one component protects against leaks, and the second against short-circuit and overloads.
Using a difavtomat, you can get rid of the situations described. It is guaranteed to turn off the network when a person directly touches equipment that is energized. Damage to the insulation and contact of live lines with the housing will also trigger this switching device.
External factor: what is the visual difference between an RCD and a residual current circuit breaker
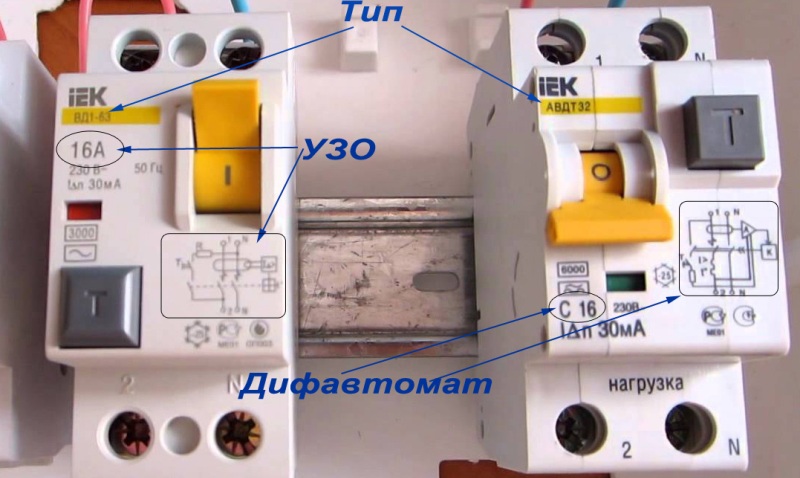
Outwardly, both devices are very similar: the body and the switch, the test button, and specific designations are similar. But more attentive comrades will immediately find the differences:
- The diagrams shown vary.
- The tumblers are different.
- Each device has its own letter designation.
We studied the functional differences above, now we will look at electrical appliances visually.
Current marking
Any node of the circuit meets certain technical characteristics. For the devices that are considered here, the main parameters are considered to be the rated leakage current and the rated operating current. For example, let's take two switches rated for 16A:
- On the RCD case, only the number (rated current) and the unit of measure - 16A are indicated in large characters.
- On the body of the difavtomat, a Latin letter is applied in front of the numbers, it can be B, C or D. For example, the letter C denotes the type of electromagnetic and thermal releases.
Electrical diagram image
To understand the difference, it is not at all necessary to study the device of each residual current device and the principle of their operation, just a careful look at the circuit on the case. At first glance, the images are similar, but we will not study the details of the circuitry - we will only define the main differences: 
- The RCD circuit contains an oval, which denotes a differential transformer that reacts to leakage. There is also an electromechanical relay that opens and closes the circuit, a contact block for connecting wires.
- On the diagram of the difavtomat, another designation is electromagnetic and thermal releases that react to short-circuit and overload currents.
Now you can easily determine the type of device by looking at the schematic diagram on the case. If releases are shown, then this is a uniquely differential machine.
Name
Some manufacturers, knowing about the problem we are analyzing, write the name on the case:
- On the side plane of the residual current device it is written - a differential switch (RCD).
- On the side of the body of the difavtomat it is written - differential current switch (RCBO).
Unfortunately, not all foreign products have such markings, but Russian manufacturers, as a rule, apply the type of apparatus. For the most part, the question of how a standard RCD differs from a residual current circuit breaker concerns foreign-made products.
Summing up the results
The cost of switching devices also differs, to a greater extent it concerns branded equipment. The price of a good difavtomat is slightly less than an RCD complete with a classic machine. 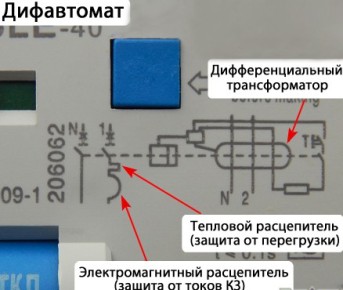
The quality of imported samples is much higher. The Russian ones are also not bad, but they are inferior in such categories as response time, mechanical stability and case quality. In terms of the reliability of operation, these devices are in no way inferior to each other.
If we take into account that the differential machine is a combined design, then of the shortcomings it is worth noting the difficulty of determining the cause of the shutdown. It is not clear what it was: current leakage, short circuit or overload. However, technologies are developing, some samples of RCBOs are already equipped with a differential current trip indicator.
A positive feature of the difavtomat is ease of installation. Sometimes, especially in a cramped flap, it is especially important to tighten two screws less. Moreover, this improves the quality of the chain assembly. However, in the event of a breakdown, the unit must only be completely replaced.
When used in an RCD circuit in tandem with a conventional automatic machine, the repair procedure is cheaper, because only one of the elements has to be changed. This point is important to consider when designing networks.
If we consider the elementary schemes of apartment wiring, then there is no fundamental difference in the choice. In a private house, you need to determine where it is more rational to insert the difavtomat, and where the residual current device is. For example, in a boiler room or workshop, the loads are large, therefore, there is a reason in the RCBO, and for the outlet lines, a set of an automatic machine and an RCD is sufficient.

